“Set” and “sit” are two commonly used verbs in English that seem similar but differ significantly in meaning and usage. Set is a transitive verb that means to place, position, or establish something deliberately, often requiring a direct object—like “set the table” or “set the alarm.” On the other hand, sit is an intransitive verb that refers to resting your weight on a surface, usually in a seated position, and does not take a direct object—such as “sit on the chair” or “sit by the window.” Lets clear the confusion about Set or Sit:
In daily conversation and writing, confusing “set” with “sit” is one of the most frequent grammar slips. This article clears the fog with easy examples, relatable explanations, and a grammar table that makes the differences impossible to forget. Perfect for students, professionals, or language enthusiasts, this guide brings confidence to your vocabulary.
Mastering set or sit adds polish to everyday communication. Whether arranging your workspace or resting after a long day, choosing the correct verb makes your sentence sound natural and grammatically accurate. Understanding these subtle differences will sharpen your language and elevate your writing.
Set Decoded: The Action Verb That Moves Things
Definition and Primary Functions
Set means to place, position, or arrange something in a specific location. This verb set meaning requires you to act upon an object. You don’t just “set” – you set something somewhere.
The use of set extends beyond simple placement. You can set an example, set goals, set records, or set boundaries. Each usage involves positioning or establishing something concrete or abstract.
Consider these English verb usage patterns:
- Physical placement: “Set the book on the table”
- Establishing conditions: “Set the temperature to 70 degrees”
- Creating standards: “Set high expectations”
- Time-related actions: “Set your alarm for 6 AM”
Set‘s Conjugation Pattern
Set follows an irregular conjugation that confuses many learners. Here’s the complete verb conjugation:
| Tense | Form | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Present Simple | set | I set the dishes daily |
| Present Continuous | setting | She’s setting the table now |
| Past Simple | set | They set the rules yesterday |
| Future Perfect | will have set | We will have set everything by noon |
This irregular pattern means set stays the same in present and past forms. Many writers incorrectly assume it changes like other verbs, leading to common grammar mistakes.
Sit Unpacked: The State of Being Verb
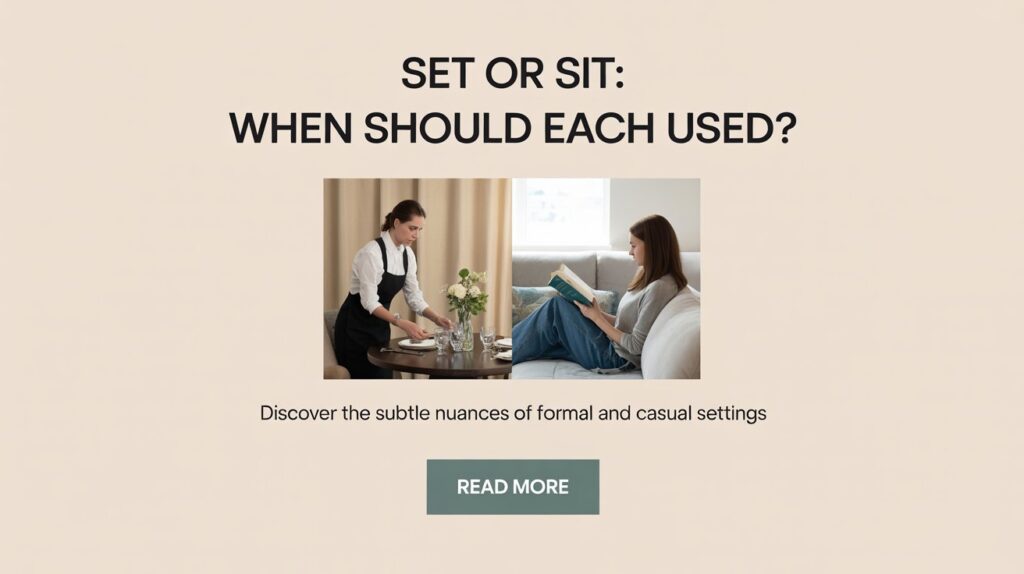
Definition and Core Usage
Sit describes the action of resting in a seated position or remaining in place. The verb sit meaning centers on position and state rather than moving objects around.
Unlike set, the use of sit doesn’t require a direct object. You simply sit. You might sit somewhere, but you’re not placing anything else.
Sit definition in English encompasses these meanings:
- Physical positioning: remaining in a seated posture
- Location-based: occupying a specific space
- Waiting or remaining: staying in one place
- Metaphorical: accepting a situation without action
Sit‘s Conjugation Journey
Sit follows a more predictable English verb usage pattern:
| Tense | Form | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Present Simple | sit | I sit in this chair |
| Present Continuous | sitting | He’s sitting quietly |
| Past Simple | sat | We sat there for hours |
| Future Perfect | will have sat | They will have sat through the meeting |
The past simple form “sat” trips up writers who incorrectly use “sit” for past actions. Remember: you sit now, but you sat yesterday.
The Memory Trick That Actually Works
S.E.T. Method: Something Else Touched
When deciding between set or sit, use this grammar tips for writers approach. SET means Something Else Touched. If your sentence involves moving, placing, or positioning an object, choose set.
Ask yourself: “Am I putting something somewhere?” If yes, you need set.
S.I.T. Method: Simply In That Spot
SIT means Simply In That spot. If you’re describing someone’s position without moving objects, choose sit.
Ask yourself: “Is someone just being in a position?” If yes, you need sit.
These memory devices help with correct verb usage and reduce English verb confusion.
Real-World Applications: Scenarios Explained

Home and Daily Life
Table setting vs sitting demonstrates the difference between set and sit perfectly. You set the table by placing dishes, utensils, and glasses. Then you sit at the table to eat.
Common household set or sit decisions:
- Set the alarm vs. sit quietly
- Set up decorations vs. sit and enjoy them
Professional Writing
Business correspondence demands precision with set and sit grammar. Professional writers must master when to use set or sit to maintain credibility.
Correct word choice examples:
- “Let’s set a meeting time” (establishing something)
- “Please sit in the conference room” (positioning yourself)
- “I’ll set the agenda” (creating/arranging)
- “We can sit tight until the decision” (waiting/remaining)
Creative Writing Applications
Fiction writers use set or sit to create vivid scenes. Contextual meaning matters enormously in creative work.
Sentence structure help for authors:
- Character actions: “She set the photograph gently on the mantle”
- Positioning: “He chose to sit by the window”
- Scene establishment: “The director set the stage for drama”
- Character state: “They sat in uncomfortable silence”
Advanced Usage: Beyond the Basics
Idiomatic Expressions
English grammar rules become complex with idioms. Many expressions use set or sit in non-literal ways.
Set idioms include:
- “Set in stone” (permanent/unchangeable)
- “Set the record straight” (clarify truth)
- “Set your mind to it” (focus determination)
Sit idioms feature:
- “Sit tight” (wait patiently)
- “Sit on the fence” (avoid choosing sides)
- “Sit well with someone” (be acceptable)
Specialized Contexts
Medical professionals use transitive and intransitive verbs precisely. A nurse might “set the patient’s arm” (position for treatment) while asking them to “sit upright” (assume a position).
Common Pitfalls and How to Dodge Them
The Parallel Problem
Set or sit confusion mirrors other confusing English words like “lay/lie” and “raise/rise.” All involve transitive and intransitive verbs.
Grammar for beginners: Remember that transitive verbs need objects, while intransitive verbs don’t.
Editing Strategies
Professional editors use these ESL grammar help techniques:
- Identify the subject in each sentence
- Look for direct objects
- Apply the S.E.T./S.I.T. memory methods
Quick Reference Tools
Decision Tree
When facing set vs sit decisions, follow this logic:
Question: Does the action involve placing/positioning something?
├── Yes → Use SET
└── No → Continue to next question
Question: Does it describe someone's position/state?
├── Yes → Use SIT
└── No → Reconsider the sentence
Conjugation Comparison Chart
| Aspect | Set | Sit |
|---|---|---|
| Type | Transitive | Intransitive |
| Needs Object | Yes | No |
| Past Form | set | sat |
| Present Participle | setting | sitting |
Test Your Mastery: Interactive Examples
Practice with these set or sit challenges:
- “Please _____ the documents on my desk.” (Set – placing objects)
- “I prefer to _____ in the back row.” (Sit – positioning yourself)
- “Let’s _____ some ground rules.” (Set – establishing something)
- “The cat likes to _____ in sunny spots.” (Sit – remaining in position)
- “We need to _____ a good example.” (Set – creating/establishing)
Each choice depends on whether you’re moving something (set) or describing position (sit).
Language Learning Strategies
English learners benefit from basic grammar guide approaches. Focus on verbs in daily life to internalize set or sit usage naturally.
Practice sentence structure help by:
- Reading aloud to hear differences
- Creating personal example sentences
- Using both verbs in writing exercises
- Studying examples in context
Etymology and Historical Context
Understanding Old English origins clarifies modern usage. Set comes from Proto-Germanic roots meaning “to cause to sit.” Sit derives from words meaning “to settle” or “remain.”
This linguistic distinction explains why set acts upon objects while sit describes states. Historical language usage patterns persist in modern English verb usage.
Frequently Asked Questions
Can “set” ever be used without an object?
Yes, in specific contexts. “The sun sets” uses set intransitively. However, most use of set requires direct objects.
What about “sit” with objects in phrasal verbs?
Phrasal verbs like “sit out” can take objects: “I’ll sit out this game.” The object belongs to the phrasal verb, not sit alone.
How do “set” and “sit” work with prepositions?
Both verbs combine with prepositions differently. You “set something down” (place it) but “sit down” (position yourself).
Are there regional differences in usage?
Set or sit usage remains consistent across English-speaking regions. However, some dialects use “set” colloquially where standard English requires “sit.”
What’s the difference between “sit down” and “set down”?
“Sit down” means assume a seated position. “Set down” means place something on a surface. The difference between set and sit remains clear even with prepositions.

Alizy Smith is a passionate language enthusiast and the admin of Grammar Wits. With a love for wordplay, grammar quirks, and witty expressions, she’s dedicated to making language learning fun and accessible. From grammar tips to pun-filled laughs, Alizy ensures every piece of content entertains while educating — turning tricky rules into easy, enjoyable reads.
